*Diagnosis
Diagnosis is made by
serologic tests and histologic
exminations, and recently, by PCR of
parasite DNA. Serologic tests such as the
ELISA, hemagglutinin, IFAT (immunofluorescent antibody test)
and Sabin-Feldman are used most commonly.
IgG and IgM antibodies can be detected 8-20 days post-infection, peak at
1-2 months, and persist for years. In the US 5-15% are seropositive,
but up to 85% are seropositive in France
and higher in developing countries.
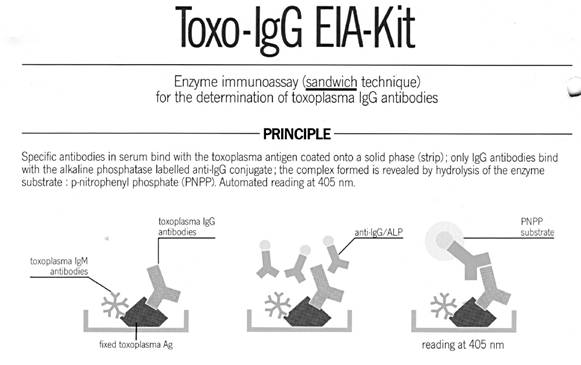
ELISA for
toxoplasmosis
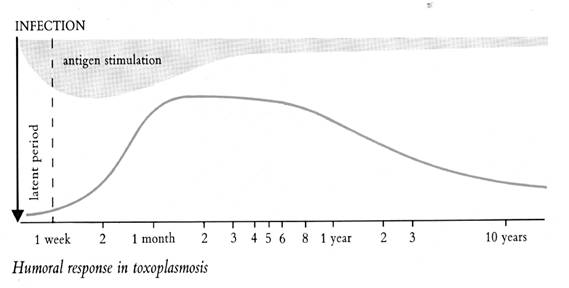
Humoral response in
toxoplasmosis
Finding of T.
gondii in microscopic examination of
stained tissues removed during biopsy or necropsy is also used diagnostically. Recovery or
identification of parasites after inoculation of biopsy material into
laboratory mice and/or cells in tissue culture. CT (computerized tomography)
scans can be useful in the diagnosis of
cerebral toxoplasmosis.
*Diagnosis by
PCR
A
PCR method was developed by Burg et al. (1989)
using as a target a 35-fold repetitive sequence,
the B1 gene. A single organism can be detected
directly from a crude cell lysate or as few as 10
parasites in the presence of 100,000 leukocytes.
Following are several
figures from the above paper showing the
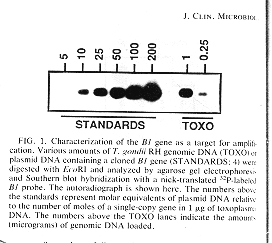
sensitivity of the method. An autoradiograph
showing that the B1 gene is 25-50 fold repetitive.
The numbers show molar equivalents of plasmid DNA
relative to moles of a single copy gene in
Toxoplasma DNA.
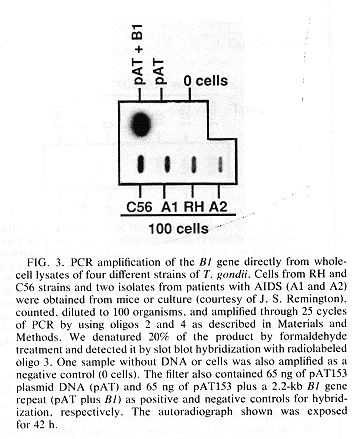
The figure below shows
PCR amplification of the B1 gene directly from
lysates of four strains of T. gondii, each
containing about 100 parasites. Slot blot
autoradiography. This shows that the B1 gene is
conserved and has about the same level of
repetition in each. No PCR products were obtained
for several related organisms which might also be
present in the patient (Plasmodium, Candida,
Aspergillus, etc.).
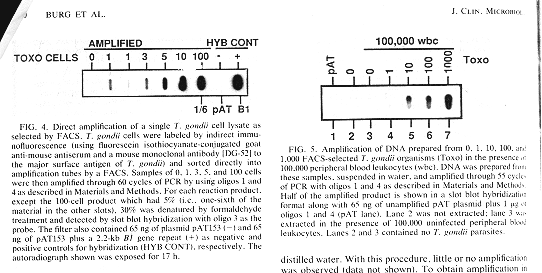
In Figure 4 below,
they used a fluorescence activated cell sorter
(FACS) to place 1,3,5, 10 and 100 T. gondii
cells into the tubes for PCR. A product could be
seen from a single cell. In Figure 5, 100,000
blood leukocytes were added to the tubes. They
could detect a signal from 10 parasites and no
product was seen from human DNA alone.
Study
question: How does the PCR diagnosis method differ
fundamentally from the immunological methods?





